Select a Size
About This Item
Halal
Kosher
Skip To
Product Name
Formic acid, ≥95%, FCC, FG
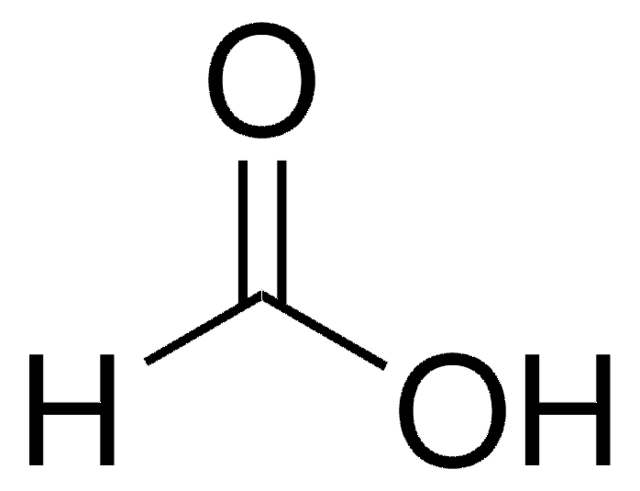
SMILES string
OC=O
InChI
1S/CH2O2/c2-1-3/h1H,(H,2,3)
InChI key
BDAGIHXWWSANSR-UHFFFAOYSA-N
biological source
synthetic
grade
FG
Halal
Kosher
agency
meets purity specifications of JECFA
reg. compliance
EU Regulation 1334/2008 & 178/2002
FCC
FDA 21 CFR 117
FDA 21 CFR 172.515
vapor density
1.6 (vs air)
vapor pressure
44.8 mmHg ( 20 °C)
assay
≥95%
form
liquid
autoignition temp.
1004 °F
expl. lim.
57 %
refractive index
n20/D 1.370 (lit.)
pH
2.2 (20 °C, 2.2 g/L)
bp
100-101 °C (lit.)
mp
8.2-8.4 °C (lit.)
density
1.22 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
anion traces
sulfate (SO42-): ≤0.004%
cation traces
As: ≤3 ppm
Cd: ≤1 ppm
Hg: ≤1 ppm
Pb: ≤10 ppm
application(s)
PFAS testing
flavors and fragrances
documentation
see Safety & Documentation for available documents
food allergen
no known allergens
organoleptic
pungent; vinegar
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
1 of 4
This Item | 695076 | F0507 | 33015 |
|---|---|---|---|
| grade FG, Kosher, Halal | grade ACS reagent | grade reagent grade | grade ACS reagent, puriss. p.a. |
| organoleptic pungent; vinegar | organoleptic - | organoleptic - | organoleptic - |
| biological source synthetic | biological source - | biological source - | biological source - |
| food allergen no known allergens | food allergen - | food allergen - | food allergen - |
| documentation see Safety & Documentation for available documents | documentation - | documentation - | documentation - |
| assay ≥95% | assay ≥96% | assay ≥95% | assay ≥98% |
Application
- Quantitative Analysis of Residual Butylated Hydroxytoluene and Butylated Hydroxyanisole in Salmo Salar, Milk, and Butter by Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry.: In this study, formic acid is used in the preparation of samples for liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis. The research focuses on the detection and quantification of antioxidant residues in food products, contributing to food safety and quality control protocols (Galal et al., 2024).
signalword
Danger
hcodes
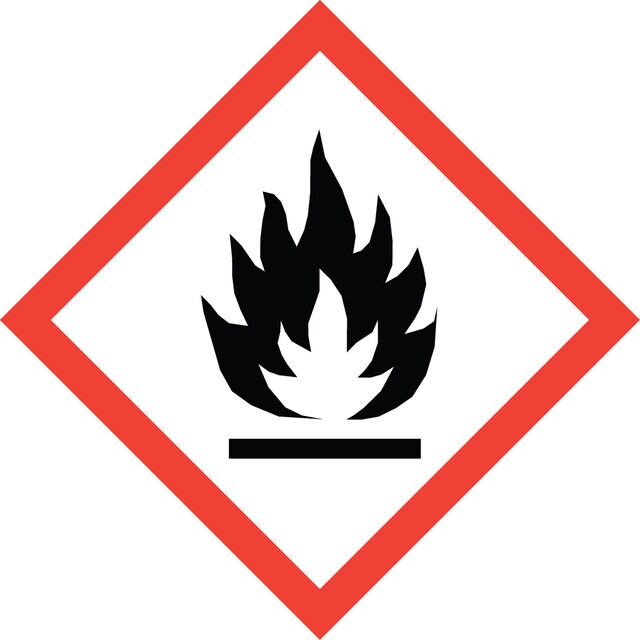
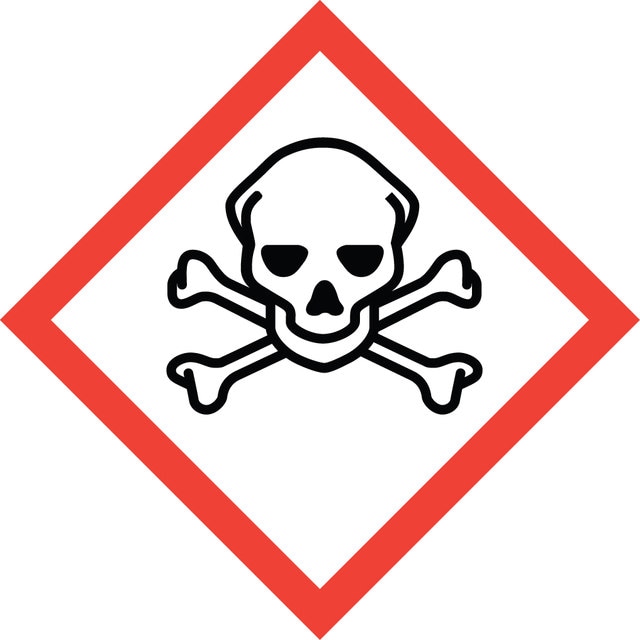
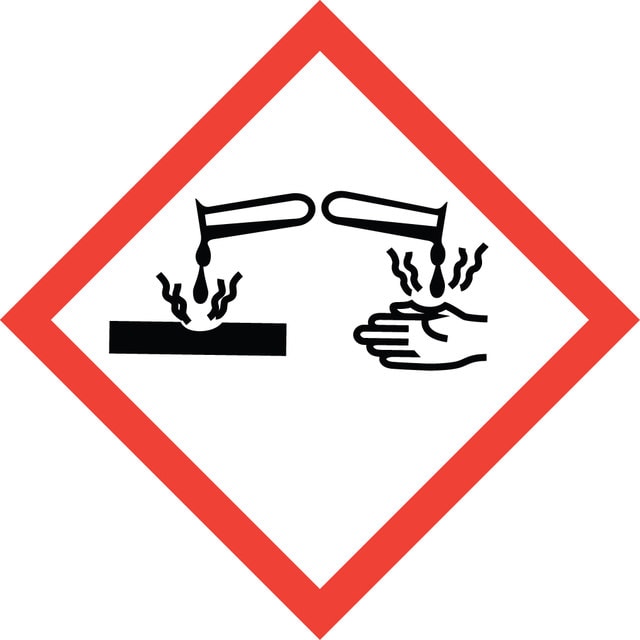
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 3 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Flam. Liq. 3 - Skin Corr. 1A
supp_hazards
Storage Class
3 - Flammable liquids
wgk
WGK 1
flash_point_f
121.1 °F - closed cup
flash_point_c
49.5 °C - closed cup
ppe
Faceshields, Gloves, Goggles, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Related Content
Active Filters
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service