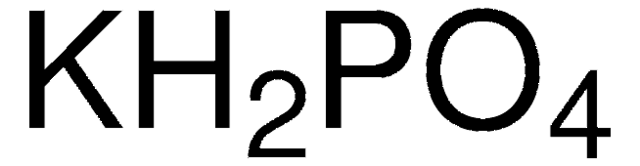Select a Size
About This Item
Skip To
Product Name
Potassium phosphate monobasic, 99.99% trace metals basis
InChI key
GNSKLFRGEWLPPA-UHFFFAOYSA-M
InChI
1S/K.H3O4P/c;1-5(2,3)4/h;(H3,1,2,3,4)/q+1;/p-1
SMILES string
[K+].OP(O)([O-])=O
assay
99.99% trace metals basis
form
solid
reaction suitability
core: potassium
impurities
≤150.0 ppm Trace Metal Analysis
pKa (25 °C)
(1) 2.15, (2) 6.82, (3) 12.38 (phosphoric acid)
mp
252.6 °C (lit.)
Quality Level
solubility
water: soluble
density
2.338 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
cation traces
Al: ≤0.3 ppm
Ca: ≤16.1 ppm
Cr: ≤0.3 ppm
Fe: ≤1.5 ppm
Mg: ≤0.2 ppm
Mn: ≤0.1 ppm
Na: ≤11.8 ppm
Rb: ≤9.6 ppm
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
1 of 4
This Item | P0662 | 60220-M | 60229 |
|---|---|---|---|
| form solid | form powder or crystals | form crystalline | form crystalline |
| assay 99.99% trace metals basis | assay ≥99.0% | assay 99.5-100.5% | assay 98-100.5% dry basis |
| Quality Level 100 | Quality Level 200 | Quality Level - | Quality Level 200 |
| density 2.338 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) | density 2.338 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) | density 2.338 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) | density 2.338 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| mp 252.6 °C (lit.) | mp 252.6 °C (lit.) | mp 252.6 °C (lit.) | mp 252.6 °C (lit.) |
| impurities ≤150.0 ppm Trace Metal Analysis | impurities ≤0.01% Insoluble matter | impurities ≤0.001% total nitrogen (N) | impurities - |
Application
- to produce flurescence emmisionin carbon dots[1]
- buffers
- pH control agent
- emulsifier
- stabilizer
- water retention agent,
- antioxidant in foods
General description
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk
WGK 1
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Active Filters
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service